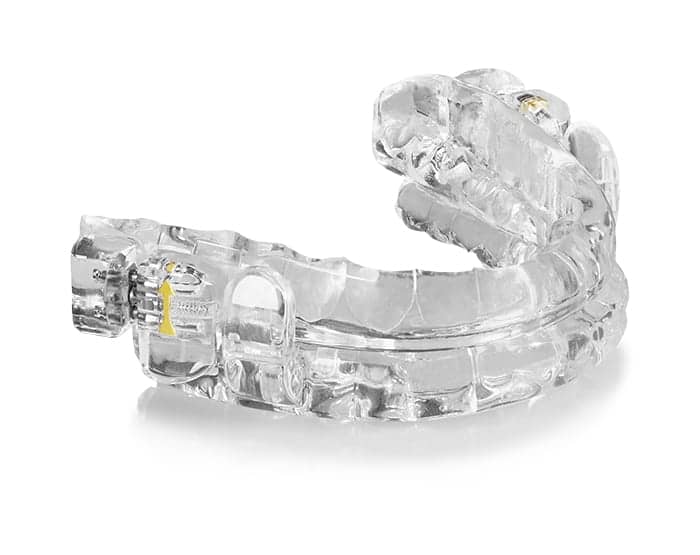
ProSomnus Inc, a developer of intraoral medical devices for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea, announced the publication of four abstracts in the Journal of Dental Sleep Medicine.
These data will be presented in oral and poster presentations at the 2023 American Academy of Dental Sleep Medicine Annual Meeting, being held from May 19 to 21 in Philadelphia.
Titles and conclusions of the accepted abstract presentations are as follows:
Precision Vs. Traditional Oral Appliance Therapy: a Comparison of Therapeutic Efficacy: Precision oral appliances appear to be more efficacious than traditional oral appliances. Further studies are required to directly compare efficacy between the two types of oral appliances and to elucidate possible causes of this apparent difference.
Comparison of Clinical Effectiveness and Patients’ Preference for Two Non-invasive Treatment Options for Patients Diagnosed with Moderate to Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea: the FLOSAT Study: In this ongoing clinical trial, mandibular advancement device therapy as a first-line treatment option showed a good efficacy in reducing the apnea-hypopnea index, combined with high patient adherence which was two hours higher as compared to the average CPAP use in an intention-to-treat analysis. This in turn resulted in a comparable overall effectiveness for mandibular advancement device therapy versus CPAP. Finally, there was a higher preference rate for mandibular advancement device compared to CPAP.
OAT Device Designs Are Not the Same When It Comes to FDA Adverse Event Reports: More adverse event reports are associated with reactions. Dental side effects infrequently result in adverse event reports. Oral appliance therapy devices that use precision-engineered materials, monolithic structures, 90-degree twin posts, and precision-engineered linerless designs are associated with lower frequencies of adverse event reports. The results of this investigation suggest that medical guidelines and insurance coding should empower therapy providers with the flexibility to prescribe devices that are associated with fewer adverse event reports.
Adverse Event Reports for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure, Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation, and Oral Appliance Therapy Devices: an FDA MAUDE Database Analysis: This analysis suggests that healthcare providers may wish to consider the significant differences in the frequencies and the severities of adverse events when prescribing treatment modalities for patients with OSA. Dental side effects, a widely referenced reason for limiting the utilization of oral appliance therapy devices, do not show up in the top 80% of the most frequently reported types of adverse events.